International Standards:
- ASME B16.9(U.S. Standard):Class 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500
- EN 10253-2(European Standard): PN6 to PN100.
- JIS B2311(Japanese Industrial Standard):5K to 40K
- GOST 17376-2001(Russian/CIS Standard): 0.1 MPa to 25 MPa
- SABS 1123(South African Standard): PN6 to PN25.
- DIN 2615 : PN6 to PN40.
- BS 1965(British Standard): PN6 to PN40.
Pros:
- Balanced Flow Distribution: Equal diameters ensure uniform flow splitting or combining.
- Simple Design: Easy to integrate into straight pipelines without complex adjustments.
- Material Versatility: Available in carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy, and plastic materials.
- High-Pressure Tolerance: Seamless tees (e.g., ASTM A234) suit high-pressure systems.
- Low Turbulence: Smooth internal surfaces minimize pressure drop in low-viscosity fluids.
Cons:
- Pressure Drop: Flow direction changes may increase resistance in high-velocity systems.
- Higher Cost: Seamless tees are more expensive than welded or cast alternatives.
- Space Requirements: Requires sufficient clearance for installation in tight layouts.
- Corrosion Risks: Welded seams may corrode in aggressive media (e.g., acids).
- Limited Flexibility: Cannot adjust flow ratios; use reducing tees for diameter changes.
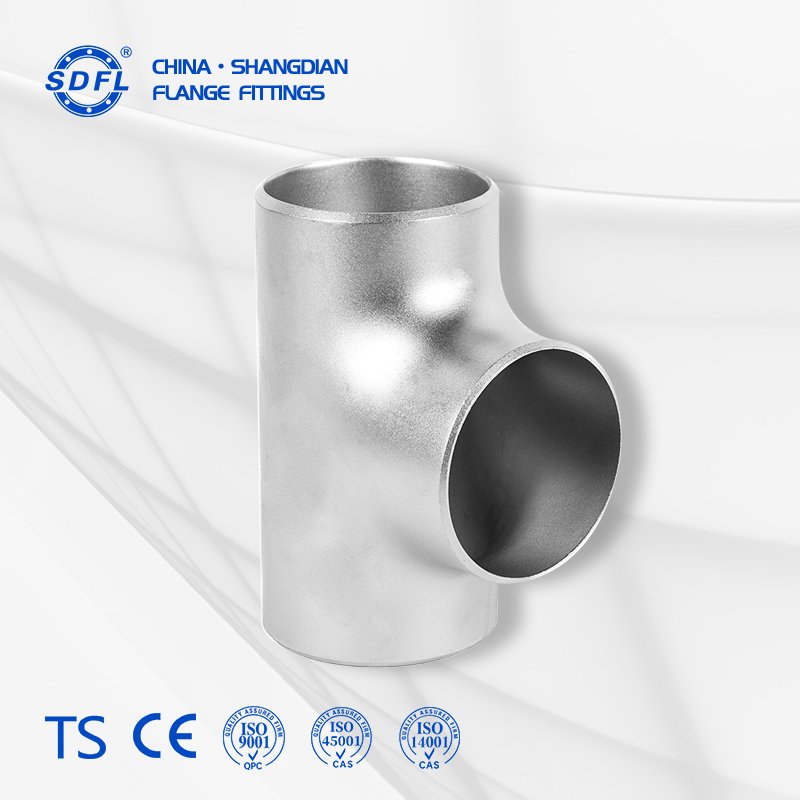
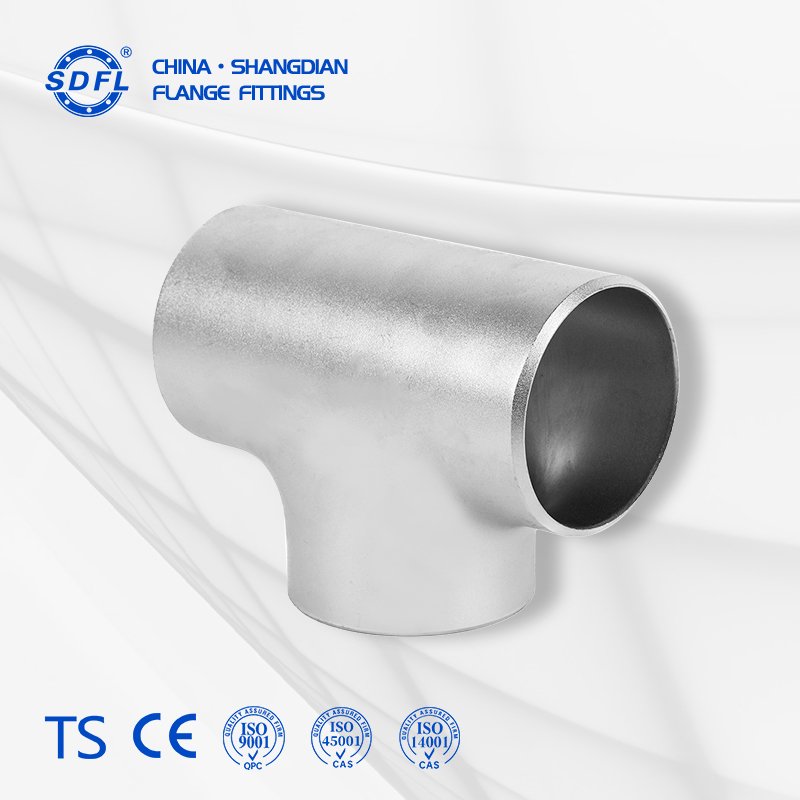
Description
An Equal Tee (or Straight Tee) is a pipe fitting with three openings of the same diameter arranged in a “T” shape. It is used to combine or split fluid flow in a pipeline, maintaining equal diameters for all branches. Equal tees are common in systems requiring balanced flow distribution, such as water supply, HVAC, and chemical processing.